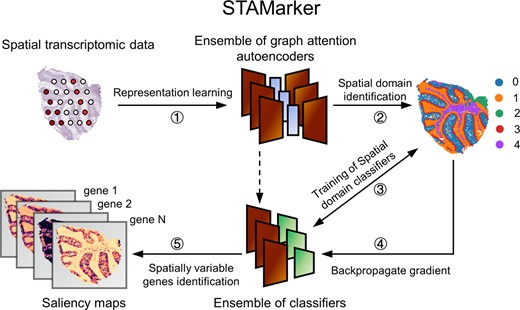
Spatial transcriptomics characterizes gene expression profiles while retaining the information of the spatial context, providing an unprecedented opportunity to understand cellular systems. One of the essential tasks in such data analysis is to determine spatially variable genes (SVGs), which demonstrate spatial expression patterns. Existing methods only consider genes individually and fail to model the inter-dependence of genes. To this end, we present an analytic tool STAMarker for robustly determining spatial domain-specific SVGs with saliency maps in deep learning. STAMarker is a three-stage ensemble framework consisting of graph-attention autoencoders, multilayer perceptron (MLP) classifiers, and saliency map computation by the backpropagated gradient. We illustrate the effectiveness of STAMarker and compare it with serveral commonly used competing methods on various spatial transcriptomic data generated by different platforms. STAMarker considers all genes at once and is more robust when the dataset is very sparse. STAMarker could identify spatial domain-specific SVGs for characterizing spatial domains and enable in-depth analysis of the region of interest in the tissue section.
Publication:
Nucleic Acids Research (Volume: 51, Issue: 20, November 2023)
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad801
Author:
Chihao Zhang
NCMIS, CEMS, RCSDS, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing,China; School of Mathematical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Kangning Dong
NCMIS, CEMS, RCSDS, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing,China; School of Mathematical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Kazuyuki Aihara
International Research Center for Neurointelligence, The University of Tokyo Institutes for Advanced Study, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Luonan Chen
Key Laboratory of Systems Biology, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai,China; Key Laboratory of Systems Health Science of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China; School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Tech University, Shanghai,China; Guangdong Institute of Intelligence Science and Technology, Hengqin, Zhuhai, Guangdong ,China
Shihua Zhang
NCMIS, CEMS, RCSDS, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China; School of Mathematical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China; Key Laboratory of Systems Health Science of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China
Email: zsh@amss.ac.cn
附件下载: